Biosensor Preparation for Nanomedicine
 Beijing
Beijing
Date: Jul.17th - Jul.21st, 2025
Subjects: Chemistry, Materials Science, Biomedicine Engneering, Nanomaterials
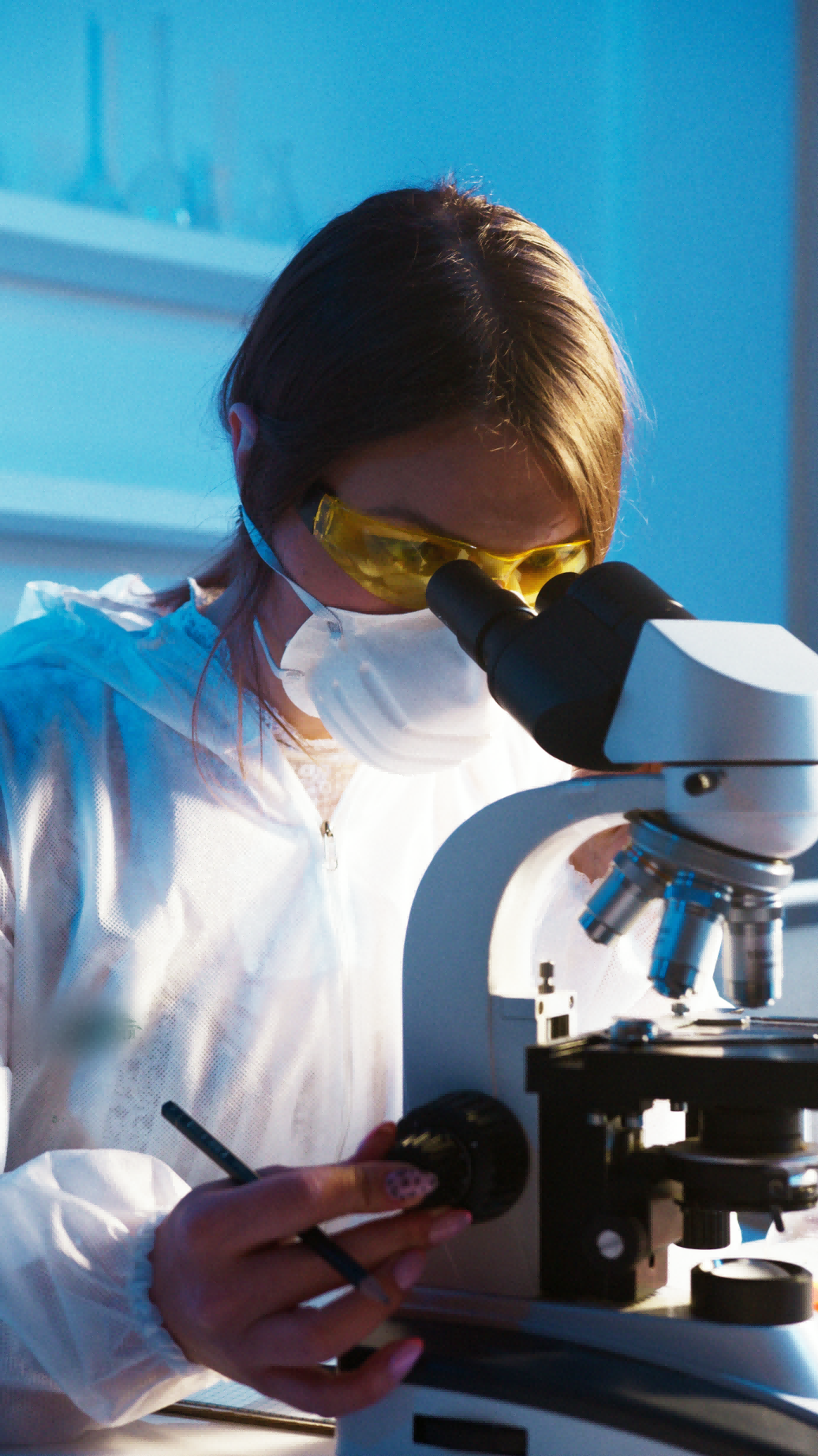

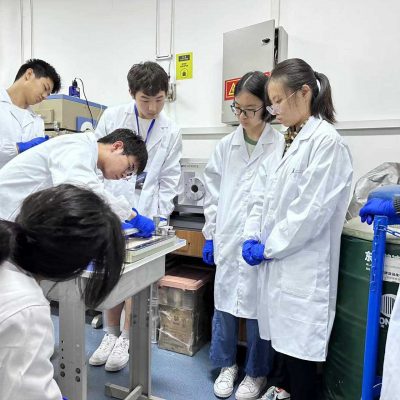
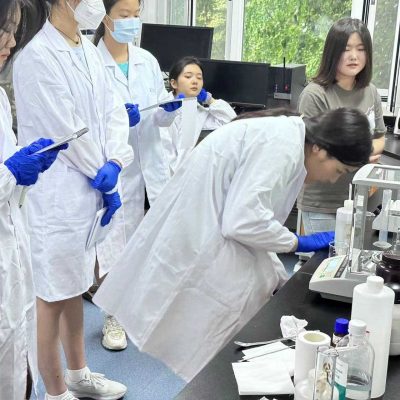
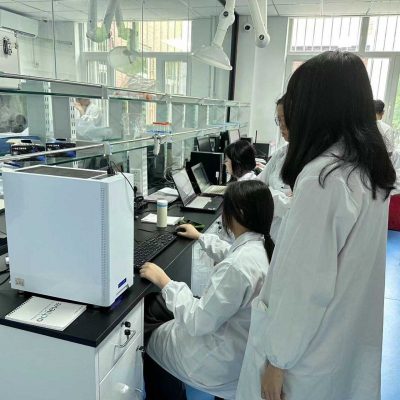
Materials science is the basis for all advanced technologies, and functional nanomaterials are one of the most dynamic areas of materials science research. Nano-biosensors are an immobilized biological component with significant advantages in the medical industry. In the case of liver cancer, patient survival after surgery depends to a great extent on accurate early diagnosis, and nano biosensors as probes enable in situ detection with great sensitivity and specificity.
This program will take you deep into the National Key Research Program in Nanotechnology at Beijing Jiaotong University to complete the identification of liver cancer markers.
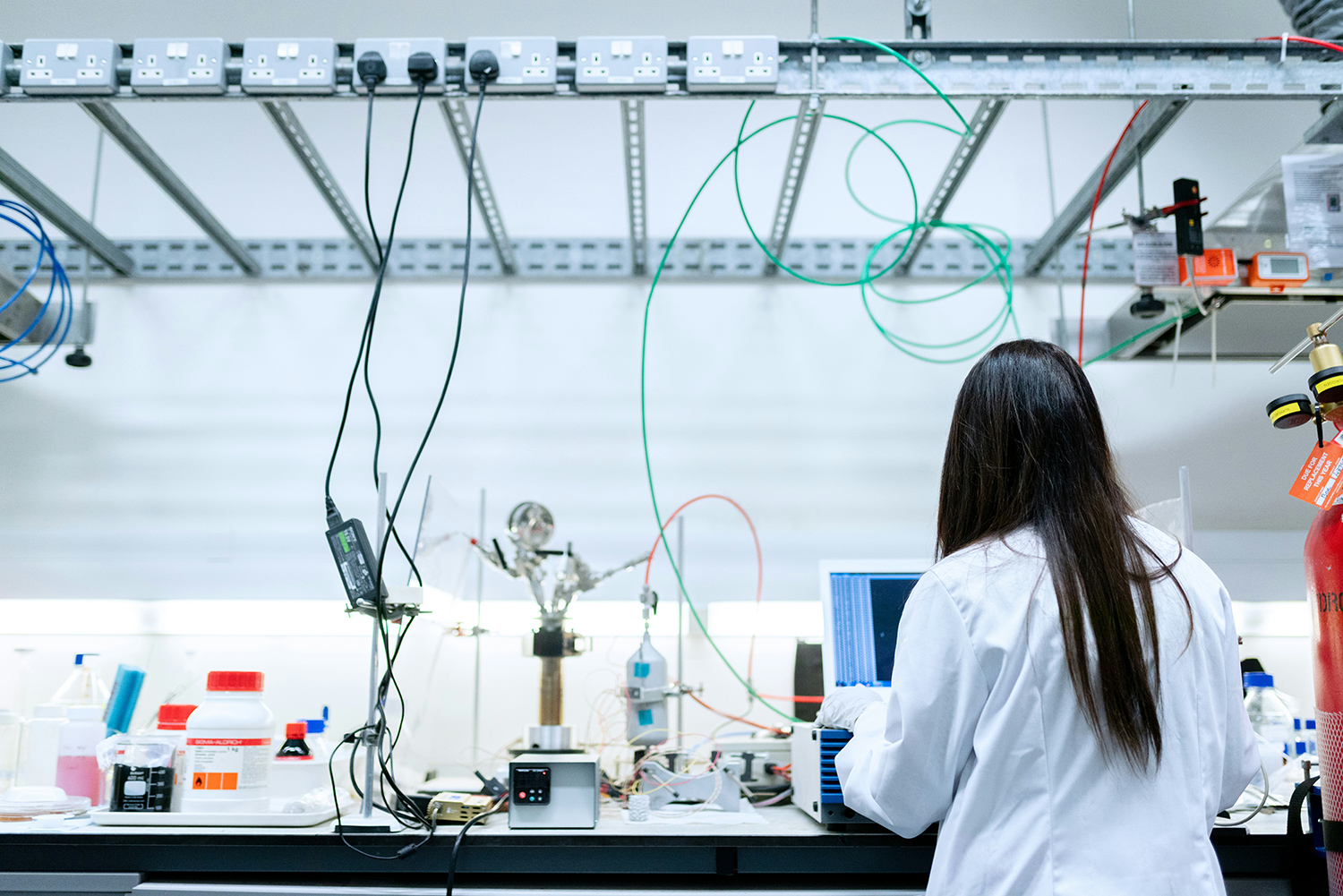

Teaching Faculty
Experts from the colleges of Science in universities of the 211 Project are specially invited.
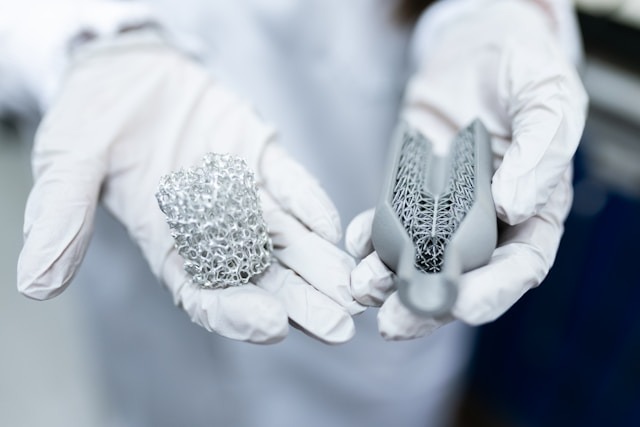

Cutting-edge Topics
Systematically learn the development of nanobiology and the application principles of nano biosensor.
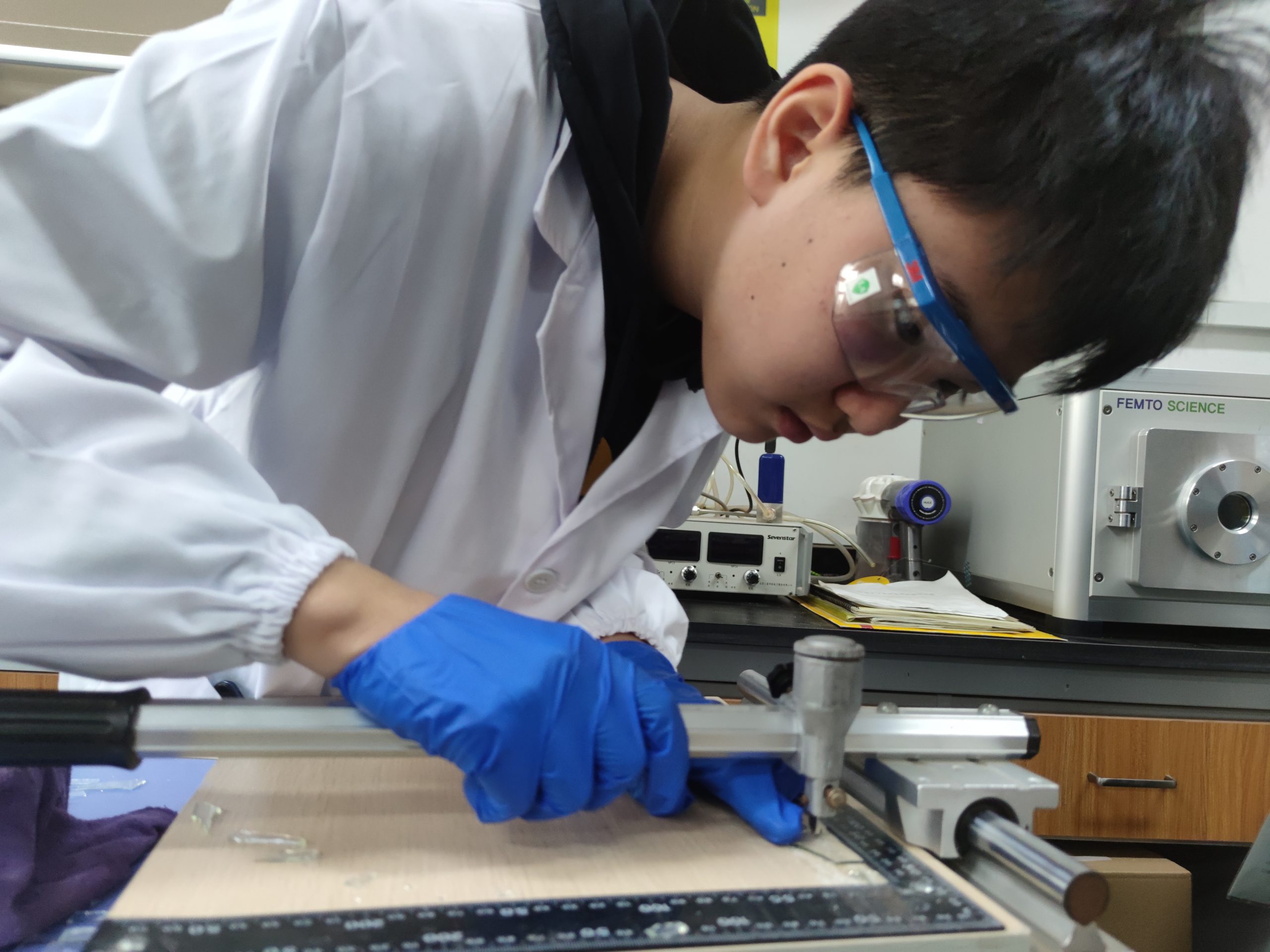

Real Lab Practice
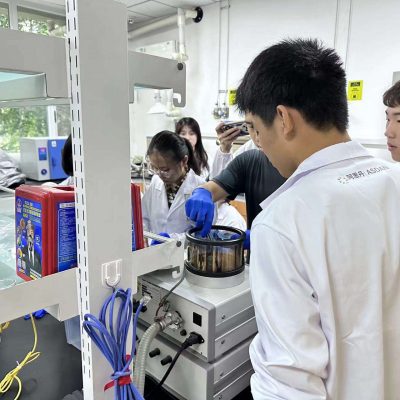
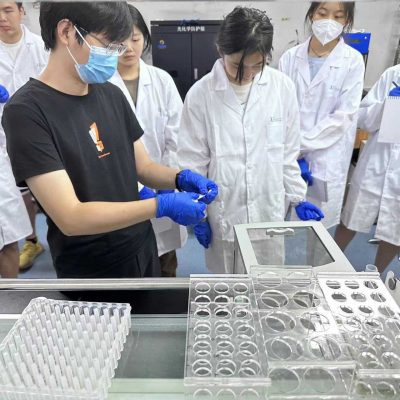
The preparation of nano-particles, microscopic morphological characterization of biosensors, etc.
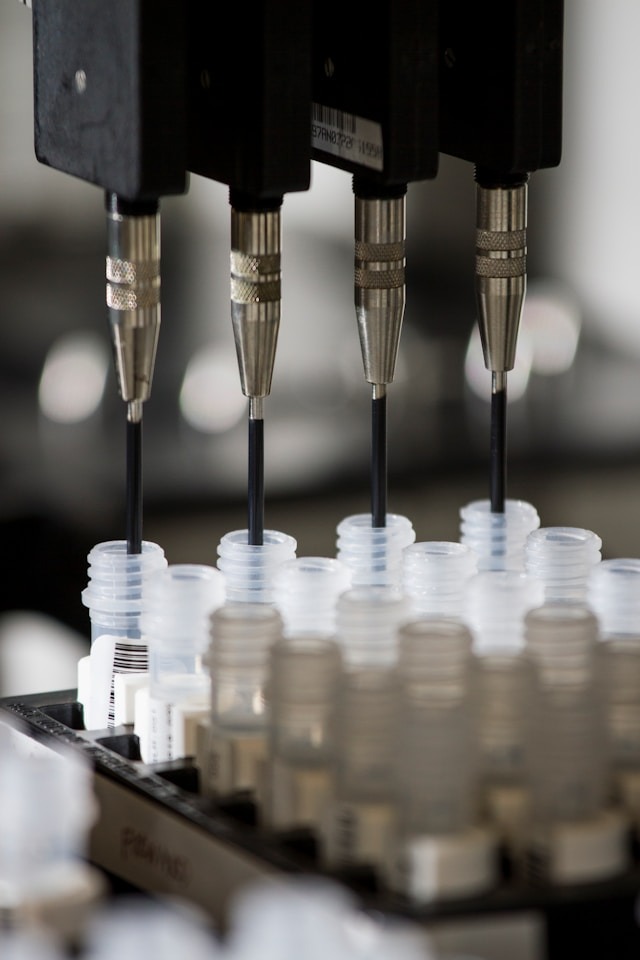

Outcome Application
Research outcomes for the earlier diagnosis of cancer in clinical medicine.
Main Experiments

Nano-electrochemical Detection
Detection of Liver Canner Marker Protein

Preparation of nanoparticles
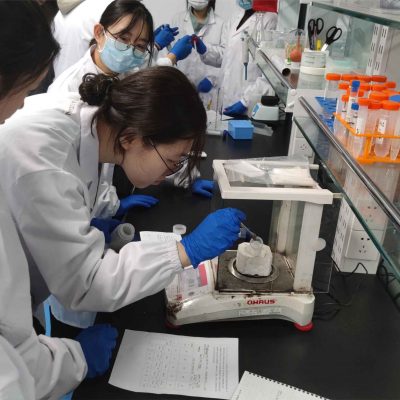
Characteristics of Biosensors
Nano-electrochemical Detection
Detection of Liver Canner Marker Protein
Preparation of nanoparticles
Characteristics of Biosensors
Certificates
).png)
CERTIFICATE OF ASDAN SCIENCE
ASDAN SCIENCE SHORT COURSES CREDIT ACCREDITED BY UCAS

CERTIFICATE OF COMPLETION ISSUED BY XLAB CHINA
Feedbacks
-

What I gained the most was the ability to manipulate instruments to conduct experiments, as I had never had direct contact with advanced instruments before this. Consequently, I had no prior understanding of them. However, this activity allowed me to manipulate these instruments, such as fluorescence microscopes, to gain initial knowledge and experimental experience. This experience and a newfound interest in chemistry experiments sparked my desire to pursue a chemistry-related major.—— Shandong Experimental High School, Student Wang

-

This activity has made me more meticulous and patient and allowed me to see many high-tech experimental machines. Both measuring experimental data and conducting experiments require precision and considerable time. We must patiently wait and ensure we recognize all experimental steps, as missing even one step could invalidate our efforts. Therefore, care and patience were the most significant takeaways from this experiment. These qualities will also greatly benefit me in future university experiments.—— Camford Royal School, Student Zhao

-

I have made many friends in this program and worked as a team to communicate more effectively. We helped each other and completed a PPT together. I also benefited a lot from learning about chemical knowledge and the use of various instrumentations. This is a significant activity because it provided me with early insights into a potential future career path in biochemistry.—— Shanghai Weiyu International School, Student Wang

Photo Gallery
Why Us
History
XLAB has a 20+ year history. It was initiated by Professor Neher of the University of Göttingen in Germany and strongly supported by the German government and the University of Göttingen. XLAB, centered around high-end scientific experiments, is widely favored by over 10,000 students yearly. XLAB has established practice centers worldwide, aiming to expand this unique concept and teaching method to reach more students.
XLAB aims to enable more people to learn and experience the joy of science, encouraging them to explore the mysteries of science and consider how to use science to solve human problems. Therefore, XALB's subjects are generally more complex in physics, biology, or medicine. Instead, they focus more on interdisciplinary, cutting-edge topics such as genetic engineering, medical research, nanobiology, medical chemistry, high-energy physics, and more.
Subject
Experiment
Experiments are the core of the XLAB. Each participant can enter advanced laboratories to conduct safe experiments, analyze data, and write experiment reports. Over six hours of scientific research daily enhances students' scientific knowledge and logical thinking and cultivates concentration and endurance. Students will be able to experience the work content and status firsthand and consider whether to choose a research direction in future education.
The courses in XLAB are unique. They consist of four key modules: Subject Introduction and Program Thinking, Scientific Research Teaching, Laboratory Operations, Experimental Data Analysis, and Research Report Writing. All courses are taught in small groups of 10 to 25 students.
Course
Faculty
Experts are invited to design experiments and teach students since the topics and content of XLAB exceed the curriculum of high schools and are specialized in specific research areas. Relevant scientific research institutions support XLAB China and provide an in-depth academic experience for Chinese students based on its unique teaching methods and experimental requirements.
Two authoritative certificates are available: the XLAB Program Certificate of Participation, which details the experimental content and is signed by instructors. Students will complete an academic report containing experimental results and data analysis to apply for the ASDAN "Science Award" Certificate for 30 credit hours of study officially accredited by UCAS.
Certificate
Research
XALB provides invaluable research scenarios for students who plan or are currently engaged in natural science research-oriented learning, such as EPQ or scientific papers, to implement their research plans and participate in hands-on scientific research. Experimental reports can be considered as part of their research achievements.










